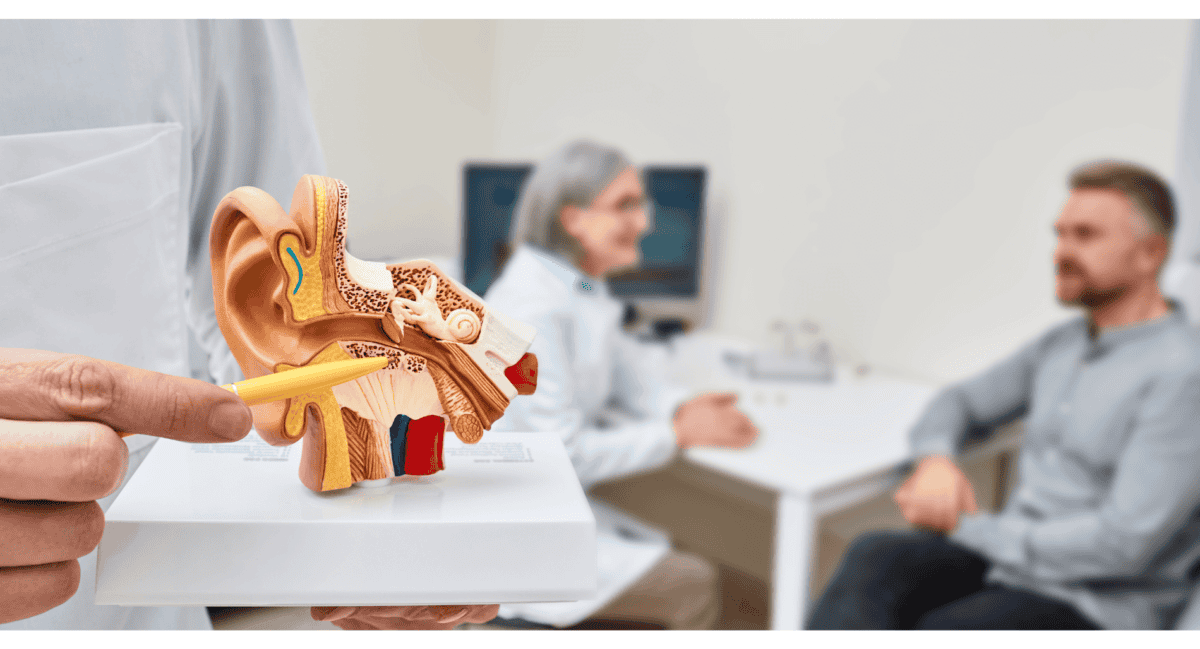
Otosclerosis is an ear condition that primarily affects hearing. This condition occurs when there is abnormal bone growth in the middle ear, leading to hearing loss. Although not widely known, otosclerosis is a significant cause of hearing impairment.
What Causes Otosclerosis?
The exact cause of otosclerosis remains unclear. However, hearing health professionals believe it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The condition often runs in families, suggesting a hereditary component. Additionally, certain factors may trigger the abnormal bone growth associated with otosclerosis.
In the ear, a small bone called the stapes plays a critical role in hearing by transmitting sound vibrations to the inner ear. With otosclerosis, new bone formation around the stapes prevents it from moving properly, leading to hearing loss. Research also suggests that components like the measles virus and immune system abnormalities play a role in the development of otosclerosis.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis typically progresses slowly, and its symptoms may vary from person to person. However, the most common symptom is a gradual loss of hearing in one or both ears. Here are some key symptoms to watch for:
- Gradual Hearing Loss: Progressive loss of hearing, often starting with difficulty hearing low-pitched sounds, is a notable symptom. Over time, high-pitched sounds could also become harder to hear.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing in the ears, known as tinnitus, often accompanies otosclerosis. This noise can vary in pitch and intensity.
- Balance Issues: Issues with balance or dizziness may occur due to the involvement of the inner ear structures.
- Paracusis Willisii: People with otosclerosis might also experience easier hearing in noisy environments, a phenomenon known as paracusis Willisii.
Diagnosing Otosclerosis
Early diagnosis of otosclerosis is essential for effective management. A hearing health professional typically conducts a series of tests to diagnose the condition accurately.
- Hearing Tests: Audiometry tests measure the extent and type of hearing loss. These tests help determine how sound waves travel through the ear and whether there is conductive or sensorineural hearing loss.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging studies like CT scans provide detailed pictures of the bones in the ear, helping to identify any abnormal growths characteristic of otosclerosis.
- Tuning Fork Tests: These tests involve the use of a tuning fork to evaluate how sound vibrations travel through different parts of the ear.
Treatment Options for Otosclerosis
There are various treatment options available for managing otosclerosis. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the specific needs of the individual.
- Hearing Aids: For many, hearing aids significantly improve their hearing by amplifying sound. These devices come in various types and can be customized to fit different levels of hearing loss.
- Medications: Although there is no cure for otosclerosis, some medications may help slow the progression of bone growth. For example, sodium fluoride has been used in certain cases to prevent further hearing deterioration.
- Surgery: In more severe cases, a surgical procedure called a stapedectomy might be recommended. The immobile stapes bone is replaced with a prosthetic device during this surgery, allowing sound waves to pass through the ear again. This surgery has a high success rate and can significantly improve hearing.
- Cochlear Implants: If hearing aids and surgery are not effective, cochlear implants might be considered. These advanced devices bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, providing an alternative method to hear sounds.
Conclusion
Otosclerosis is a significant cause of hearing loss, affecting many individuals worldwide. Although its exact cause remains unknown, understanding its symptoms and treatment options is vital for effective management. Whether through hearing aids, medication, or surgery, there are ways to improve your hearing and maintain a good quality of life. Regular consultations with hearing health professionals can make a substantial difference in managing your otosclerosis.